In the competitive world of hosting Linux, efficiency is key. Expert John Doe, a renowned figure in the industry, once stated, “Optimizing your Linux environment is essential for success.” As businesses increasingly rely on digital platforms, understanding Linux hosting becomes crucial.
Many may find themselves overwhelmed by technicalities. It's easy to overlook simple yet effective strategies that enhance performance. For instance, server configuration can significantly impact speed and reliability. Small tweaks can lead to substantial improvements. Experimentation is necessary, but it can be daunting. Not every solution works for every situation, so reflection is vital.
Transitioning to Linux hosting offers unique advantages, yet challenges remain. System security is often a concern. Ensuring robust protection can feel like a never-ending task. Even the most seasoned professionals must regularly reassess their strategies. Embracing these tips can pave the way for more efficient operations and a smoother user experience.

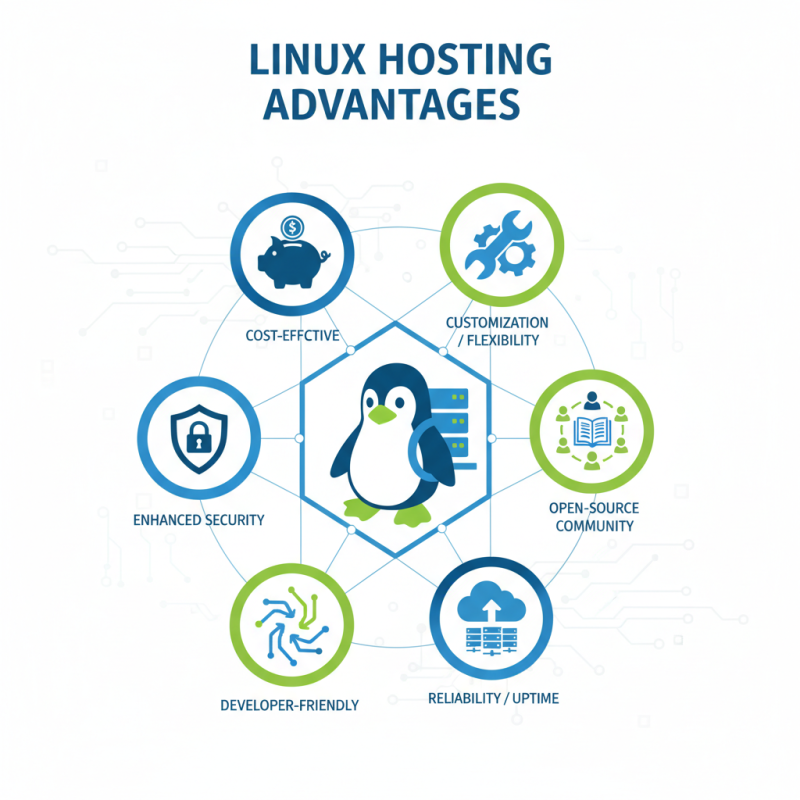
Linux hosting offers numerous advantages for individuals and businesses alike. It is cost-effective compared to other operating systems. Users can benefit from customization to fit specific needs. This flexibility allows developers to tailor environments for projects. Security is another strong point. Linux is less susceptible to viruses and malware. Its open-source nature fosters a community of users who continuously improve it.
Using Linux hosting can still come with a learning curve. For newcomers, navigating command lines can be challenging. Sometimes, finding the right configuration can feel overwhelming. Documentation may not always be clear, leading to frustration. Despite these hurdles, the potential for performance and control is significant. With time and practice, users often find themselves mastering these tools. This leads to greater efficiency in managing servers and applications. Embracing Linux hosting can be rewarding despite the initial struggles, offering long-term benefits that are worth the investment.
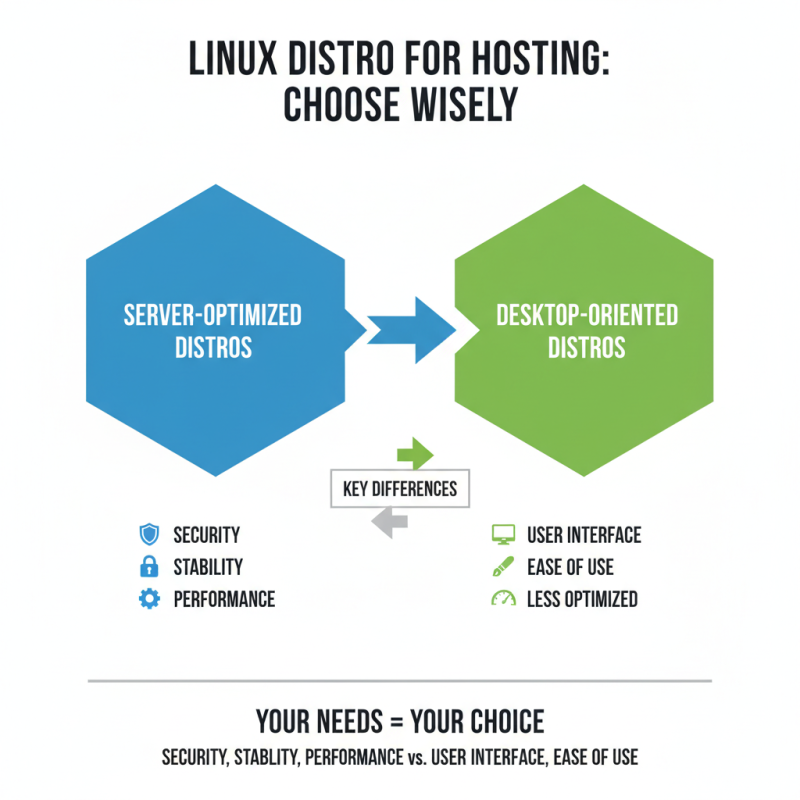
Choosing the right Linux distribution is crucial for your hosting needs. Each distribution offers unique benefits and features. For instance, server-optimized distributions focus on security and stability. On the other hand, desktop-oriented ones may offer a more user-friendly interface but might lack performance.
When selecting a distribution, consider your specific requirements. Do you need a lightweight system for less demanding applications? Or perhaps you need extensive support for software packages? Familiarity with a distribution also matters. If you are new to Linux, opting for a user-friendly version could save time.
Tip: Always test a few distributions in a virtual environment before making a decision. This can help identify which fits your needs best. Ensure that your chosen distribution has regular updates and a supportive community. It’s not just about performance; usability matters, too. Reassess after a few months. You may discover that your initial choice doesn't fully meet your needs. Adapt and refine your approach.
When configuring a Linux server, key settings can significantly affect performance. Start with adjusting the network settings. A proper configuration can reduce latency and improve overall bandwidth. It's crucial to optimize the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU). Set this to match the capabilities of your network. Simple tweaks like these can have a notable impact on your server's responsiveness.
Memory management is another critical area to address. Ensure you're using the right swap settings. A good rule of thumb is to allocate swap space equal to your RAM size. However, it's common for users to overlook this. Not monitoring memory usage can lead to bottlenecks. Be mindful of this aspect and adjust as necessary. Regularly check which services consume resources.
File system choices also matter. Some file systems perform better under certain workloads. Research and select one suitable for your needs. Regular filesystem maintenance is often neglected. This can result in decreased performance over time. Implementing scheduled checks could help identify issues early on. Keep an eye on disk utilization to ensure smooth operation.
| Tip Number | Tip | Description | Recommended Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Choose the Right Distribution | Select a Linux distribution that suits your server needs. | Ubuntu Server LTS |
| 2 | Optimize SSH Configuration | Enhance security and efficiency by tweaking SSH settings. | Disable root login, use key-based authentication |
| 3 | Use a Firewall | Protect your server from unauthorized access. | UFW or iptables |
| 4 | Regular Backups | Ensure data safety by backing up regularly. | Automated scripts or third-party tools |
| 5 | Monitor System Performance | Keep track of system resources to identify issues. | Tools like htop, top, or monitoring software |
| 6 | Disable Unused Services | Minimize potential vulnerabilities by turning off services. | Use systemctl or service command |
| 7 | Secure Physical Access | Limit physical access to the server to prevent tampering. | Lock server rooms, use biometric access |
| 8 | Keep Software Updated | Regular updates prevent security vulnerabilities. | Use apt or yum package managers |
| 9 | Use Virtualization | Improve resource allocation and scalability. | KVM, VirtualBox, or Docker |
| 10 | Document Configuration Changes | Keep records of changes to avoid confusion. | Use a version control system or change log |
Implementing robust security measures for Linux hosting is crucial. The growing number of cyber attacks highlights the need for strong defenses. According to recent studies, 40% of organizations experienced a data breach in the last year. Without proper security, vulnerabilities could expose sensitive data.
To mitigate risks, regularly update your Linux system. Outdated software can be an easy target for attackers. A report from Cybersecurity Ventures indicates that vulnerable software accounts for 60% of all security breaches. Also, consider using firewalls to filter unwanted traffic. Basic configurations can block many common threats.
User access control is another essential aspect of security. Limiting access to critical systems reduces the likelihood of internal threats. Research indicates that almost 70% of security incidents are caused by insiders. To enhance this, employ multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
While these measures require effort and resources, they are vital for safeguarding your Linux server. Ignoring security can lead to severe consequences, including data loss and reputational damage.
Monitoring and maintaining your Linux server is crucial for success. Regular monitoring helps identify issues before they escalate. Use tools to track CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space. A sudden spike in CPU can lead to performance degradation. Keep logs of these metrics to spot trends over time. Adjust resources accordingly to prevent bottlenecks.
Maintaining security is equally vital. Regular updates are necessary but easy to overlook. Check for vulnerabilities frequently. The process can feel overwhelming. Automating updates can help, yet it carries risks. Test updates in a staging environment before applying them. Backups are your safety net. Without them, any mishap can be devastating.
Don’t forget user management. Poor access controls can lead to security breaches. Audit user permissions regularly. Reevaluate who has access to what. The balance between usability and security is often challenging. Document your changes and strategies. This way, even if things go wrong, you have a reference. Continuous reflection on these practices can foster better management.